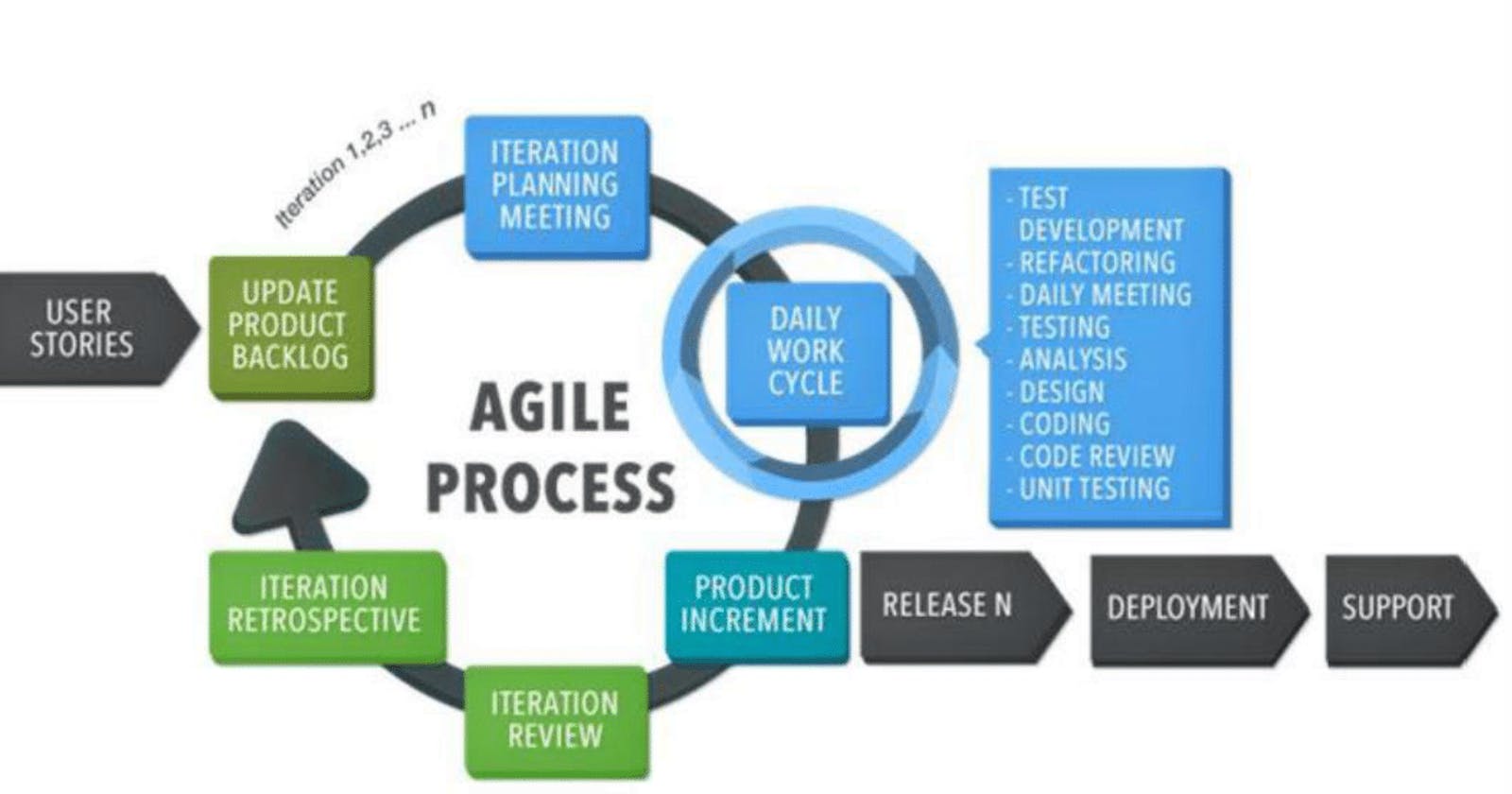
AgileScrum-Blog#03 ScrumMaster's Role
A Servant Leader, Role as Overall, in Daily StandUp, Notes:{SAFe, Lean-Agile Process, ART}
Ragnar Lodbrok is working as Scrum Master in Jarotball (Company) and during the Daily stand-up, what would be his most preferred role among followings:
- [ ] Congratulate the team on their great work.
- [x] Stand outside the circle of developers and listen for impediments.
- [ ] The Scrum Master should not attend—this meeting is for developers only.
- [ ] Ask each developer what they did since the last daily standup.
1. Scrum Master - is a servant leader
Good leaders must first become good servants. —Robert K. Greenleaf
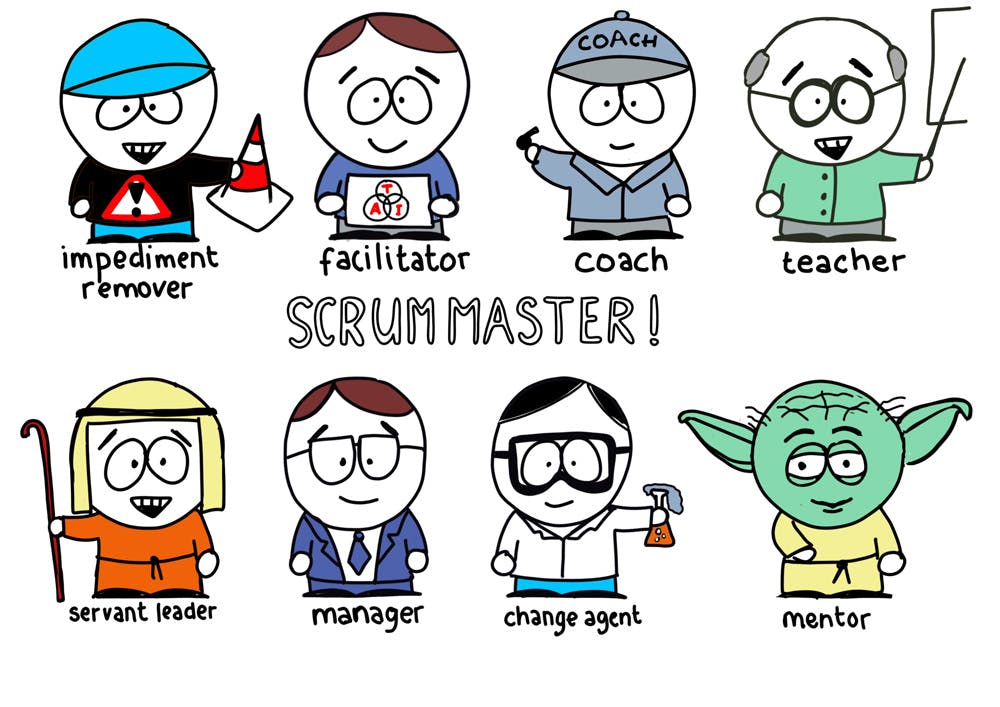
The Scrum Master role is taken by a team member whose primary responsibility is assisting the self-organizing, self-managing team to achieve its goals by
- teaching and coaching team practices,
- educate the team in Scrum, Extreme Programming (XP), Kanban, and SAFe
- implementing and supporting SAFe principles and practices,
- The Scrum Master also helps the team coordinate with other teams on the Agile Release Train (ART).
- identifying and eliminating impediments, and facilitating flow.
- ensuring that the agreed Agile process is being followed
This person spends much of their time in
- helping other team members communicate, coordinate, and cooperate;
- generally, this person assists the team in meeting their delivery goals.
Questions the Scrum Master may ask include:
- What did you accomplish yesterday?
- What will you accomplish today?
- Is anything holding you back?
1.1 Scrum Master Role (Overall)
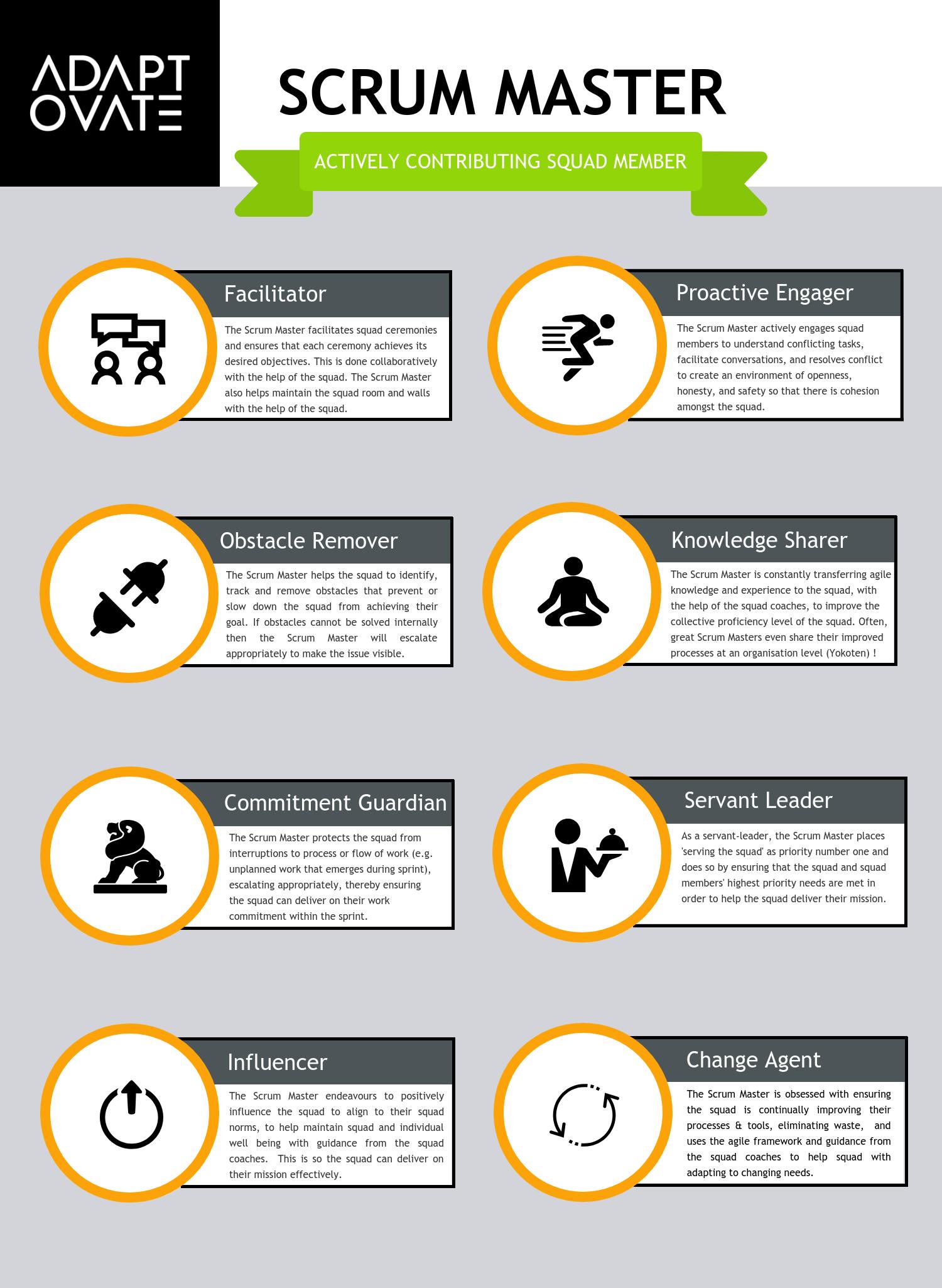
- Exhibits Lean-Agile leadership
- Supports the team rules
- Facilitates the team’s progress toward team goals
- Leads team efforts in relentless improvement
- Facilitates events
Supports the Product Owner
- The Scrum Master helps the Product Owner in their efforts to manage the backlog and guide the team while facilitating a healthy team dynamic with respect to priorities and scope.
Facilitates the removal of impediments
- Many blocking issues will be beyond the team’s authority or may require support from other teams.
- The Scrum Master supports the team in addressing and eliminating these issues to improve the likelihood of achieving the objectives of the Iteration.
- Promotes SAFe quality practices
- Builds a high-performing team
- Responsibilities on the train
- Coordinates with other team -They frequently represent the team in the Scrum of Scrums (SoS)
- Supports SAFe adoption
- Enables organizational effectiveness
- Facilitates preparation and readiness for ART events
- Supports estimating features and capabilities
1.2 Scrum Masrer Role in Daily Standup

- The Scrum Master ensures that the meeting happens, but the Developers are responsible for conducting the Daily Scrum.
- The Scrum Master teaches them to keep the Daily Scrum within the 15-minute time-box.
The Daily Scrum is an internal meeting for the Scrum Team. If others are present, the Scrum Master ensures that they do not disrupt the meeting. Note: The Daily Scrum is Not a Status Meeting.
NOTE 01: SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) Principle
The impression that ‘our problems are different’ is a common disease that afflicts management the world over. They are different, to be sure, but the principles that will help to improve the quality of product and service are universal in nature. —W. Edwards Deming
- SAFe provides guidance to assist the teams in constantly improving the quality of their deliverables and meeting the Definition of Done (DoD).
SAFe Lean-Agile Principles:
SAFe is based on ten immutable, underlying Lean-Agile principles. These tenets and economic concepts inspire and inform the roles and practices of SAFe.
- Take an economic view
- Everyday decisions must be made in a proper economic context
- This includes the strategy for incremental value delivery and the broader economic framework for each value stream, which highlights
- trade-offs between risk,
- Cost of Delay (CoD),
- manufacturing, operational, and
- development costs
- Apply systems thinking
- Assume variability; preserve options
- Build incrementally with fast, integrated learning cycles
- Base milestones on objective evaluation of working systems
- Visualize and limit WIP, reduce batch sizes, and manage queue lengths
- Apply cadence, synchronize with cross-domain planning
- Unlock the intrinsic motivation of knowledge workers
- Lean-Agile leaders understand that ideation, innovation, and employee engagement are not generally motivated by individual incentive compensation.
- Bad Approach- Such individual incentives can create internal competition and destroy the cooperation necessary to achieve the larger aim of the system.
- Good Approach- Providing autonomy and purpose, minimizing constraints, creating an environment of mutual influence, and better understanding the role of compensation are keys to higher levels of employee engagement. This approach yields better outcomes for individuals, customers, and the enterprise.
- Decentralize decision-making
- Organize around value
- Many enterprises today are organized around principles developed during the last century. In the name of intended efficiency, most are organized around functional expertise.
- Bad way to organize around values - But in the digital age, the only sustainable competitive advantage is the speed with which an organization can respond to the needs of its customers with new and innovative solutions. These solutions require cooperation amongst all the functional areas, with their incumbent dependencies, handoffs, waste and delays.
- Good way to organizae around values - Instead, Business Agility demands that enterprises organize around value to deliver more quickly. And when market and customer demands change, the enterprise must quickly and seamlessly reorganize around that new value flow.

NOTE 02: Lean-Agile Process
- What is Lean? Lean encourages teams to deliver fast by managing flow, limiting the amount of WIP (work-in-process) to reduce context switching and improve focus.
- What is Agile? Agile teams manage flow by working in cross-functional teams on delivering one iteration at a time.
- A truly Lean-Agile process incorporates elements of both continuous delivery and continuous improvement,optimized across the entire value stream.
- Kaizen focuses on improving processes that enable Agile teams and organizations to reach their goals of frequent, iterative value delivery.
Note 03: Agile Release Train (ART)
- The Agile Release Train (ART)
- is a long-lived team of Agile teams,
- which, along with other stakeholders, incrementally develops, delivers, and
- where applicable operates, one or more solutions in a value stream.
Value Stream: A value stream is the set of actions that take place to add value to a customer from the initial request through realization of value by the customer. The value stream begins with the initial concept, moves through various stages of development and on through delivery and support.
Value-stream mapping: also known as "material- and information-flow mapping", is a lean-management method for analyzing the current state and designing a future state for the series of events that take a product or service from the beginning of the specific process until it reaches the customer.
2. Solving Question through Elimination Strategy
- [ ] Congratulate the team on their great work. [S01: This is not a Scrum for Scrum Master]
- [ ] Stand outside the circle of developers and listen for impediments. [S02: Tentative Right Answer for Now]
- [ ] The Scrum Master should not attend—this meeting is for developers only. [S03: Definitely he should attend the meeting]
- [ ] Ask each developer what they did since the last daily standup. [S04: Scrum Daily Standup is Not a STATUS Meeting]
2.1 Answer
Q2. Ragnar Lodbrok is working as Scrum Master in Jarotball (Company) and during the Daily stand-up, what would be his most preferred role?
- [x] Stand outside the circle of developers and listen for impediments.
Final Thought
Elite Scrum Masters should act as a servant/leaders, a coach, and a facilitator. They will know exactly how to change hats depending on the context and situation. It is through training, daily practice, and experience that you can reach the elite level and create a culture of thriving Scrum teams.