AgileScrum-Blog#01 Agile Methodology: A Brief Summary
Scrum, XP, Agile Vs Waterfall, Lean, Kanban and Rugby!!!!
1. Agile as English Word
In English, Agile means ‘ability to move quickly and easily’ and responding swiftly to change – this is a key aspect of Agile software development as well.
2. Adobe is Developing Microsoft Word !!!! - Scenario
Adobe is working on project to come up with a competing product for Microsoft Word, that provides all the features provided by Microsoft Word and any other features requested by the marketing team. The final product needs to be ready in 10 months of time. Let us see how this project is executed in traditional and Agile methodologies.
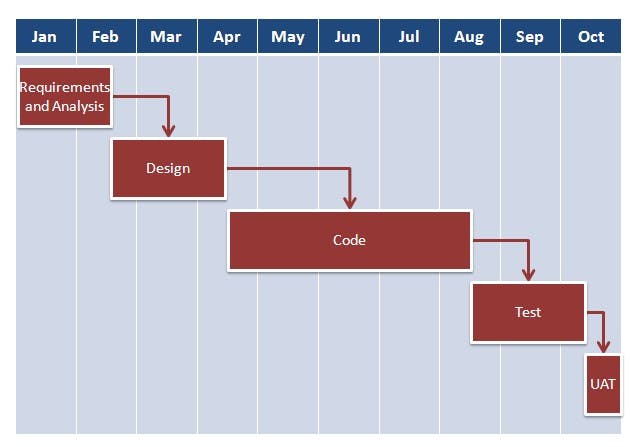
2.1 In traditional Waterfall model
- At a high level, the project teams would spend 15% of their time on gathering requirements and analysis (1.5 months)
- 20% of their time on design (2 months)
- 40% on coding (4 months) and unit testing
- 20% on System and Integration testing (2 months).
- At the end of this cycle, the project may also have 2 weeks of User Acceptance testing by marketing teams.
- In this approach, the customer does not get to see the end product until the end of the project, when it becomes too late to make significant changes.
2.2 With Agile development methodology
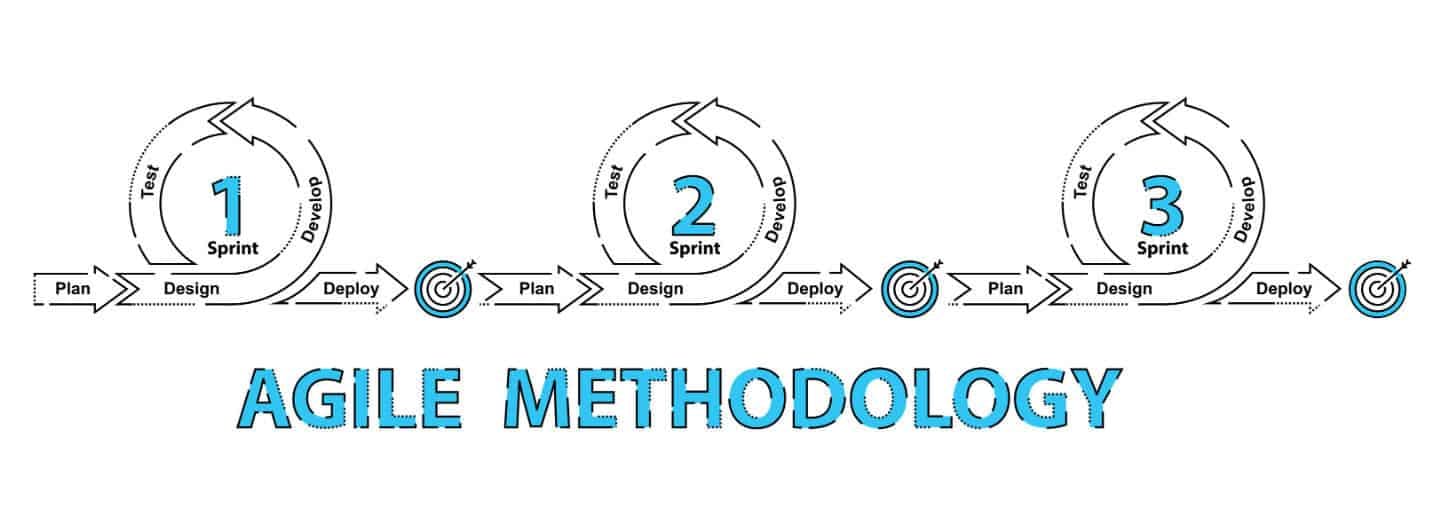
- In the Agile methodology, each project is broken up into several ‘Iterations’.
- All Iterations should be of the same time duration (between 2 to 8 weeks).
- At the end of each iteration, a working product should be delivered.
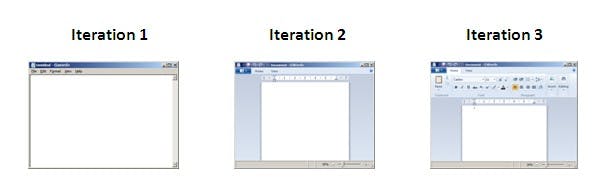
- In simple terms, in the Agile approach the project will be broken up into 10 releases (assuming each iteration is set to last 4 weeks).
- Rather than spending 1.5 months on requirements gathering, in Agile software development, the team will decide the basic core features that are required in the product and decide which of these features can be developed in the first iteration.
- Any remaining features that cannot be delivered in the first iteration will be taken up in the next iteration or subsequent iterations, based on priority.
- At the end of the first iterations, the team will deliver a working software with the features that were finalized for that iteration.
- There will be 10 iterations and at the end of each iteration the customer is delivered a working software that is incrementally enhanced and updated with the features that were shortlisted for that iteration.
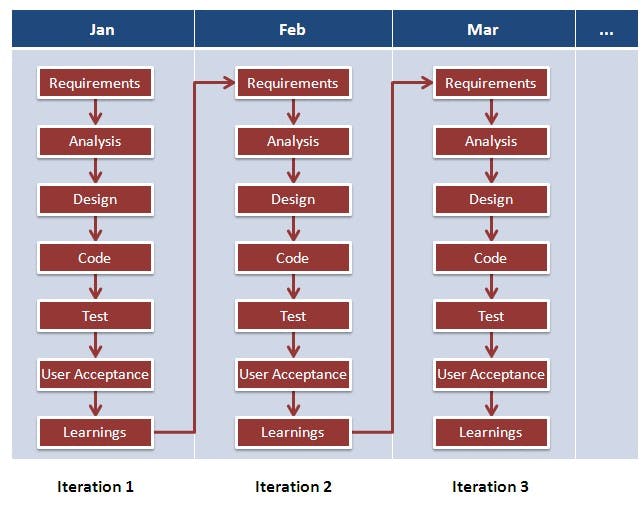
This approach allows the customer to interact and work with functioning software at the end of each iteration and provide feedback on it. This approach allows teams to take up changes more easily and make course corrections if needed. In the Agile approach, software is developed and released incrementally in the iterations. An example of how software may evolve through iterations is shown in the image below.
3. What is Agile Methodology?

AGILE methodology is a practice that promotes continuous iteration of development and testing throughout the software development lifecycle of the project. In the Agile model, both development and testing activities are concurrent, unlike the Waterfall model.
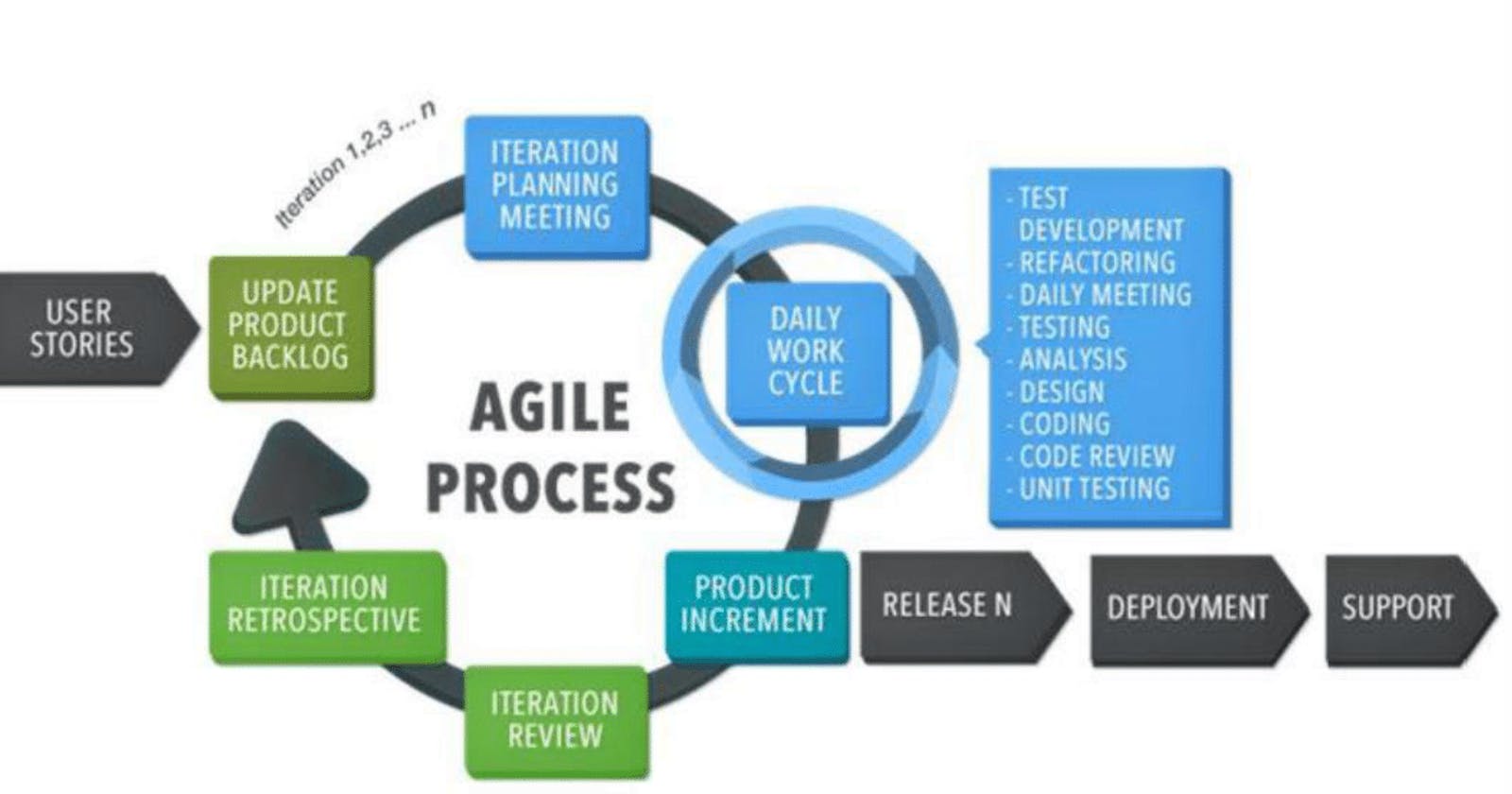
3.1 Agile Process
Check below Agile process model to deliver successful systems quickly.
There are various Agile methods present in agile testing, and those are listed below:
3.1.1 Scrum
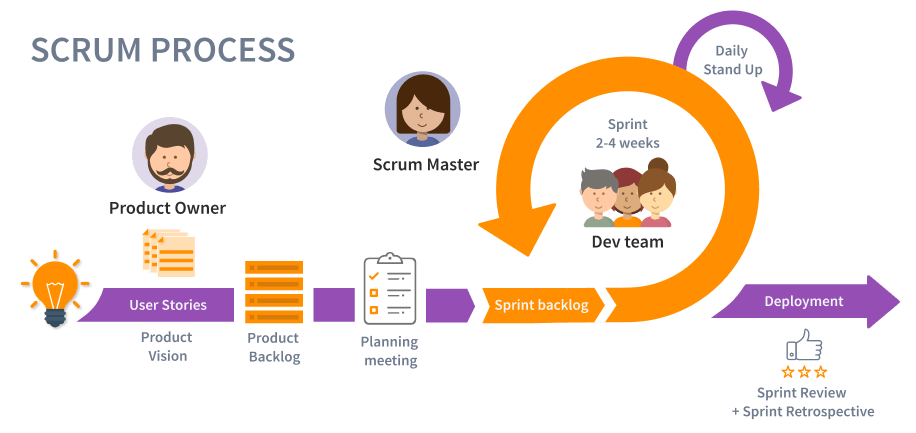
 SCRUM is an agile development method which concentrates specifically on how to manage tasks within a team-based development environment. Basically, Scrum is derived from activity that occurs during a rugby match. Scrum believes in empowering the development team and advocates working in small teams (say- 7 to 9 members). It consists of three roles, and their responsibilities are explained as follows:
SCRUM is an agile development method which concentrates specifically on how to manage tasks within a team-based development environment. Basically, Scrum is derived from activity that occurs during a rugby match. Scrum believes in empowering the development team and advocates working in small teams (say- 7 to 9 members). It consists of three roles, and their responsibilities are explained as follows:
- Scrum Master: Master is responsible for setting up the team, sprint meeting and removes obstacles to progress
- Product owner: The Product Owner creates product backlog, prioritizes the backlog and is responsible for the delivery of the functionality at each iteration
- Scrum Team: Team manages its own work and organizes the work to complete the sprint or cycle
Product Backlog This is a repository where requirements are tracked with details on the no of requirements(user stories) to be completed for each release. It should be maintained and prioritized by Product Owner, and it should be distributed to the scrum team. Team can also request for a new requirement addition or modification or deletion.
Scrum Practices Practices are described in detailed:
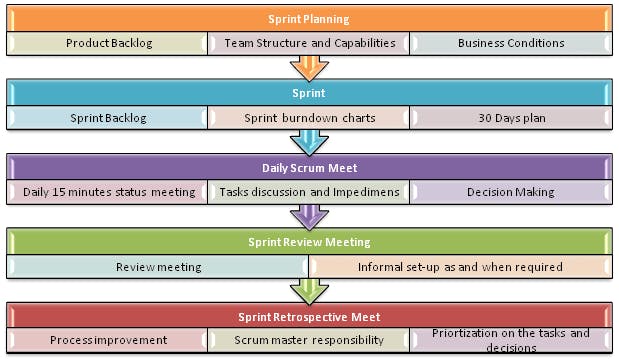
Process flow of Scrum Methodologies Process flow of scrum testing is as follows:
- Each iteration of a scrum is known as Sprint
- Product backlog is a list where all details are entered to get the end-product
- During each Sprint, top user stories of Product backlog are selected and turned into Sprint backlog
- Team works on the defined sprint backlog
- Team checks for the daily work
- At the end of the sprint, team delivers product functionality
3.1.2 eXtreme Programming (XP)
Extreme Programming technique is very helpful when there is constantly changing demands or requirements from the customers or when they are not sure about the functionality of the system. It advocates frequent "releases" of the product in short development cycles, which inherently improves the productivity of the system and also introduces a checkpoint where any customer requirements can be easily implemented. The XP develops software keeping customer in the target.
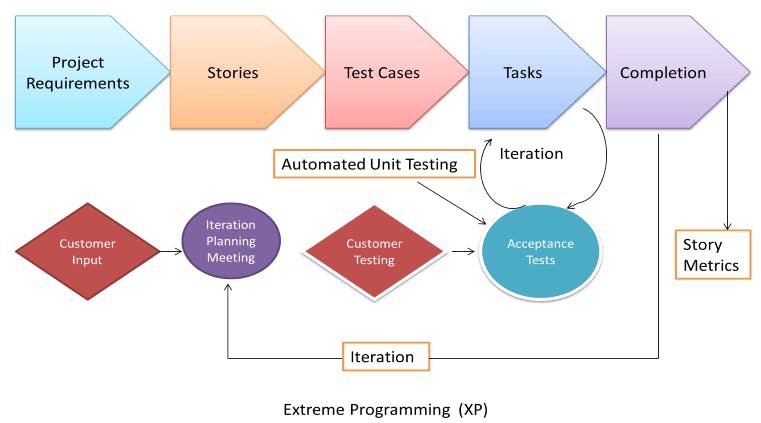
Business requirements are gathered in terms of stories. All those stories are stored in a place called the parking lot.
In this type of methodology, releases are based on the shorter cycles called Iterations with span of 14 days time period. Each iteration includes phases like coding, unit testing and system testing where at each phase some minor or major functionality will be built in the application.
3.1.3 Crystal Methodologies
Crystal Methodology is based on three concepts: (a) Chartering (b) Cyclic delivery (c) Wrap up
3.1.4 Dynamic Software Development Method (DSDM)
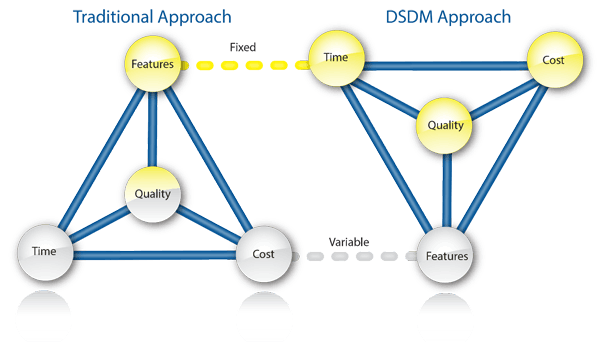 DSDM is a Rapid Application Development (RAD) approach to software development and provides an agile project delivery framework. The important aspect of DSDM is that the users are required to be involved actively, and the teams are given the power to make decisions. Frequent delivery of product becomes the active focus with DSDM.
DSDM is a Rapid Application Development (RAD) approach to software development and provides an agile project delivery framework. The important aspect of DSDM is that the users are required to be involved actively, and the teams are given the power to make decisions. Frequent delivery of product becomes the active focus with DSDM.
The techniques used in DSDM are: Time Boxing, MoSCoW Rules and Prototyping. The DSDM project consists of 7 phases: Pre-project, Feasibility Study, Business Study, Functional Model Iteration, Design and build Iteration, Implementation, Post-project.
MoSCoW (Must Have, Should Have, Could Have, Won't Have this time) is primarily used to prioritise requirements, although the practice is also useful in many other areas.
3.1.5 Feature Driven Development (FDD)
This method is focused around "designing & building" features. Unlike other agile methods, FDD describes very specific and short phases of work that has to be accomplished separately per feature. It includes domain walkthrough, design inspection, promote to build, code inspection and design.
3.1.6 Lean Software Development
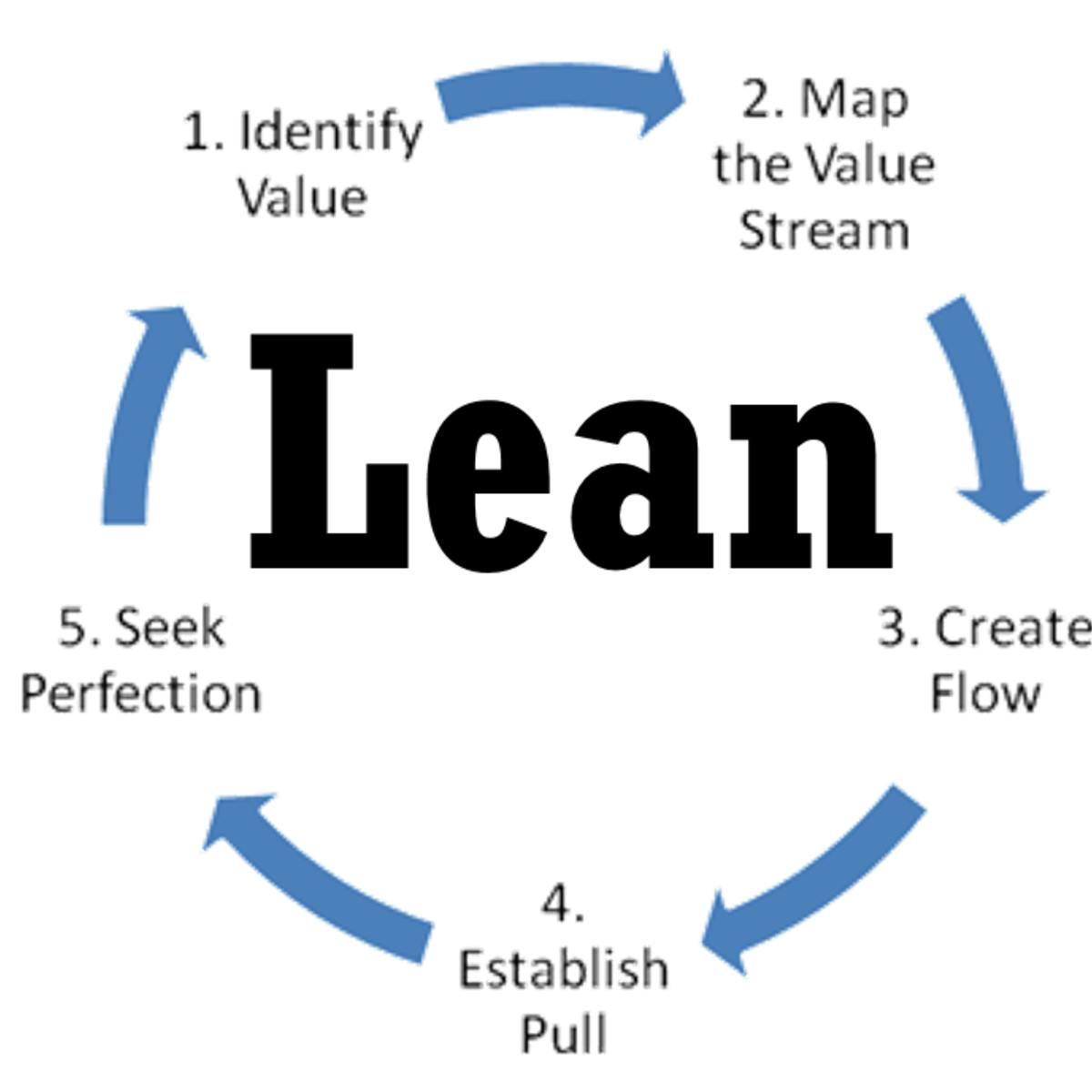 Lean software development method is based on the principle "Just in time production". It aims at increasing speed of software development and decreasing cost. Lean development can be summarized in seven steps.
Lean software development method is based on the principle "Just in time production". It aims at increasing speed of software development and decreasing cost. Lean development can be summarized in seven steps.
- Eliminating Waste
- Amplifying learning
- Defer commitment (deciding as late as possible)
- Early delivery
- Empowering the team
- Building Integrity
- Optimize the whole
3.1.7 Kanban
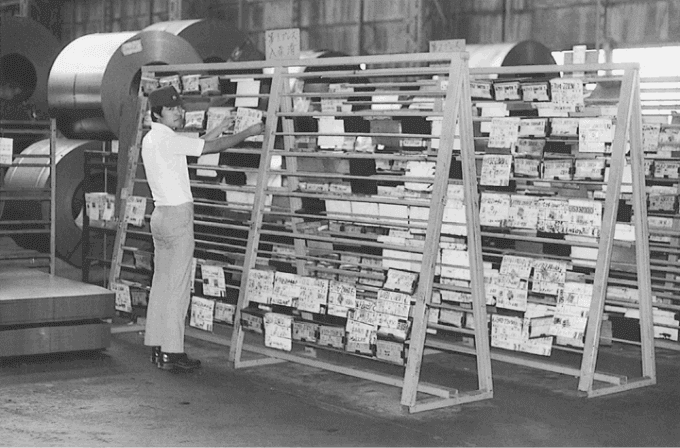 Kanban originally emerged from Japanese word that means, a card containing all the information needed to be done on the product at each stage along its path to completion. This framework or method is quite adopted in software testing method especially in agile testing.
Kanban originally emerged from Japanese word that means, a card containing all the information needed to be done on the product at each stage along its path to completion. This framework or method is quite adopted in software testing method especially in agile testing.
Kanban has these six core practices:
- Know and visualize your current flow.
- Limit the Work In Progress (WIP).
- Clear process policies.
- Manage workflow.
- Regular feedbacks.
- Optimizing and evolving (using models and the scientific method).
List of Top 5 Open Source Kanban Software Kanban board software is a widely used task management tool. And if you are already using one, you must be aware of all of its features to help you to better monitor and control multiple projects according to team or project’s needs.
There are a lot of kanban tools and apps in the market right now. Currently, Trello, Asana, Monday.com, Kanbanize, and Blossom are amongst the most popular kanban tools.
Here, I will enlist the five most popular open-source kanban tools that are worth using.
4. Scrum Vs Kanban
| Scrum | Kanban |
| In scrum technique, test must be broken down so that they can be completed within one sprint | No particular item size is prescribed |
| Prescribes a prioritized product backlog | Prioritization is optional |
| Scrum team commits to a particular amount of work for the iteration | Commitment is optional |
| Burndown chart is prescribed | No particular item size is prescribed |
| Between each sprint, a scrum board is reset | A Kanban board is persistent. It limits the number of items in workflow state. Having too high WIP limits means that your team is probably working on multiple tasks, switching context all the time, and not meeting the deadlines. multitasking is deceptively time-intensive. |
| It cannot add items to ongoing iteration | It can add items whenever capacity is available |
| WIP limited indirectly ** work in progress (WIP) limits set the maximum amount of work that can exist in each status of a workflow. Limiting the amount of work in progress makes it easier to identify inefficiency in a team's workflow. | WIP limited directly |
| Timeboxed iterations prescribed | Timeboxed iterations optional |
5. Agile Metrics
Metrics that can be collected for effective usage of Agile is:
A. Drag Factor
- Effort in hours which do not contribute to sprint goal
- Drag factor can be improved by reducing number of shared resources, reducing the amount of non-contributing work
- New estimates can be increased by percentage of drag factor -New estimate = (Old estimate+drag factor)
B. Velocity
- Amount of backlog(user stories) converted to shippable functionality of sprint
C. No of Unit Tests added
D. Time interval taken to complete daily build
E. Bugs detected in an iteration or in previous iterations
F. Production defect leakage
6. Agile Methodology Tools
The list below shows some of the best tools on offer. For a complete list, see this post.
- ActiveCollab. An affordable tool for small businesses, ActiveCollab is easy to use. This software development aid requires little training and provides excellent support.
- Agilo for Scrum. Stakeholders get updated automatically on the project’s progress with Agilo for Scrum. Features sprint reports and burn down charts for better data mining.
- Atlassian Jira + Agile. This powerful project management tool facilitates development by incorporating Scrum, Kanban, and customizable workflows.
- Pivotal Tracker. This methodology tool is geared specifically for mobile projects. A little jargon-heavy, it’s user-friendly after a brief orientation period.
- Prefix. This free tool from Stackify provides an instant feedback loop to catch and fix bugs before they can deploy.
- Retrace. For a more robust solution complete with monitoring, errors, logs, and more, Stackify’s Retrace provides app performance insights from integration to QA to production, at the code level.
7. Additional Resources
Make use of the non-product style tools and resources for success below, including the original Agile manifesto and a few downloadable templates for implementation.
- Agile Manifesto . This is the original document that kicked off the Agile movement. It contains all 12 key tenets of the methodology at large.
- Burn Down Charts. These are visual representations of work left vs remaining time. Download an Excel template here from SmartSheet.com
- Agile project plan . This is a tool for tracking the progress of the overall Agile project. This article from Ambysoft outlines the entire project planning process.
- Agile product backlog. This helps product owners track and prioritize customer requirements. You can download an Excel template template here.