ServerlessArchitecture#05 - Various Scenarios in which timeouts can lead to BAD User Experiences
If you work on a serverless project, you have probably run into the issue of AWS Lambda timeouts handling. Lambda functions are short lived; the Lambda max timeout is 900 seconds (15 minutes). This can be difficult to manage and can cause issues in production applications.
We’ll take a look at AWS Lambda timeout limits, timeout errors, monitoring timeout errors, and how to apply best practices to handle them effectively.
To summarize, the blog Use-Cases are:
- What are the AWS Lambda Timeout Limits? - 6 Best Practices To Handle Lambda Timeout Errors
- Monitoring Lambda Timeout Errors with CloudWatch and X-Ray
- AWS Lambda Timeout Deep Dive: Three Scenarios to Understand Timeout Behavior
- Scenario 01: A REST API implemented through a Lambda Function is exposed through API Gateway.
- Scenario 02: REST API is calling multiple services. It’s calling a DynamoDB table to retrieve data, calling an API, and then storing the data back in the DynamoDB table.
- Scenario 03: A bad approach: use a fixed AWS Lambda timeout limit at the function and integration level hardcoded in the code/config.
SUMMARY
What does Timeout mean in AWS Lambda - A Summary Before Deep Drive
When the specified timeout is reached, AWS Lambda terminates execution of your Lambda function. As a best practice, you should set the timeout value based on your expected execution time to prevent your function from running longer than intended.
- The maximum timeout for a Lambda function is 900 seconds at the time of this publication.
which means a single invocation of a Lambda function cannot execute longer than 900 seconds.
- A Guide For You: You should not always set the timeout for a Lambda function to the maximum
There are many cases where an application should fail fast.
- Please Remember: your Lambda function is billed based on execution time in 100-ms increments
Avoiding lengthy timeouts for functions can prevent you from being billed while a function is simply waiting to timeout.
Waiting to Timeout!! WHY?- perhaps an external dependency is unavailable, you’ve accidentally programmed an infinite loop, or another similar scenario.
- Before Timeout reaches Ensure Followings:
- Also, once execution completes or a timeout occurs for your Lambda function and a response is returned, all execution ceases.
- This includes any background processes, subprocesses, or asynchronous processes that your Lambda function might have spawned during execution.
- So you should not rely on background or asynchronous processes for critical activities.
- Your code should ensure those activities are completed prior to timeout or returning a response from your function.
Never Forget: Lambda functions are meant to be small and quick rather than large applications
Lets Consider a Scenario
Jahidul Arafat has developed a Lambda Function and when he deploy and test it, it throws the following error
Error Message: Task timed out after 6.01 seconds
Type: LOG EVENT
Severity: CRITICAL
Now, as a Cloud Specialist, Debug the Potential Cause of it.
Hello Mr. Debugger
A. Why do I see this?
AWS intentionally stopped a function invocation once it hit a run-time of X seconds.
B. What does this mean?
Lambda functions are limited to a maximum execution time of 15 minutes. A custom limit can be configured when the Lambda function is created. The limit is in place because Lambda functions are meant to be small and quick rather than large applications.
C. How do I fix if Lambda task is timed out?
Enable AWS X-ray tracing to get a breakdown of the execution. You can also log out the function’s main activities to understand the timescale and identify bottlenecks inside a function execution.
| How to Fix | Strategy |
| Increase the timeout limit | The time limit is defined in function configuration and can easily be modified. The maximum limit set by AWS is currently 15 minutes. |
| Simplify the function | A well-written function usually only does one thing. If you’re executing multiple actions in a single function, it can be useful to consider decoupling that function and breaking it up between multiple functions. |
| Don’t orchestrate/wait in code | If you’re waiting for a task to execute inside the function or using a function to coordinate between more than one additional task, there is a significant risk that you’ll end up accumulating additional costs and risking timing out. This is not aligned with the best practices of serverless. Consider orchestrating with step functions. |
1.1 What are AWS Lambda Timeout Limits?
A Lambda Serverless application is made up of three major components. Each of these components can time out, affecting your serverless application:
- Event source – commonly the AWS API Gateway
- Lambda function – affected by service limits of AWS Lambda
- Services – other resources the Lambda function integrates with, commonly DynamoDB, S3, and third party apps.
The following table summarizes the timeout limits and important considerations for each component.
| Serverless Component | Max Timeout | Comments |
| API Gateway | 50 milliseconds – 29 seconds | Configurable |
| Lambda Function | 900 seconds (15 minutes) | Also limited to 1,000 concurrent executions. If not handled, can lead to throttling issues. |
| DynamoDB Streams | 40,000 write capacity units per table | |
| S3 | No timeout by default, can be configured to 5-10 seconds | Unlimited objects per bucket |
| Downstream Applications | Check your applications |
1.2 6 Best Practices To Handle Lambda Timeout Errors
| Practices | Description |
| Use short timeout limits for event sources | set timeout to 3-6 seconds for API calls. - For Kinesis, DynamoDB Streams or SQS you should adjust the limits based on the batch size. |
| Monitor Lambda function timeouts | put monitoring in place using CloudWatch and X-Ray and fine tune the timeout values as applicable. |
| Use fallback methods | if timeouts are unavoidable, either return the response with error code and description or use fallback methods. - Fallback methods can use cached data or get data from an alternative source - check out Hystrix or Spring Retry for Java or oibackoff lib for Node.js |
| Avoid exceeding DynamoDB write capacity | if you increase concurrent executions for your function, avoid exceeding the 40,000 writes limit. - Use node-rate-limiter in Node.js. |
| Optimize your function | if your function is running longer than the desired timeout value, check the steps that the function is performing. - If you are doing too many things in one function, consider Step Functions to break it into smaller pieces. |
| Balance performance and cost | To increase performance, Lambda gives only a single option – increase memory. More memory equals more CPU. There are a few common scenarios: - If a function logic is CPU intensive, add memory to reduce the execution time. It not only saves cost but also reduces timeout errors. - If a function spends most of its time on DB operations, there is no point in increasing memory. It won’t help. - Add memory to bring execution time below the nearest 100. AWS charges for Lambda usage in increments of 100ms. For example: if average execution is 110ms, increase memory to bring it below 100ms, or you’ll be charged for 200ms. |
1.3 Monitoring Lambda Timeout Errors with CloudWatch and X-Ray
There are two AWS-native solutions you can use to monitor logs for Lambda – CloudWatch and X-Ray.
CloudWatch
CloudWatch provides Duration metrics which tell us how much time a Lambda function is taking throughout a particular period. It also tells us the Average Duration which can be used to baseline the function timeout limit.
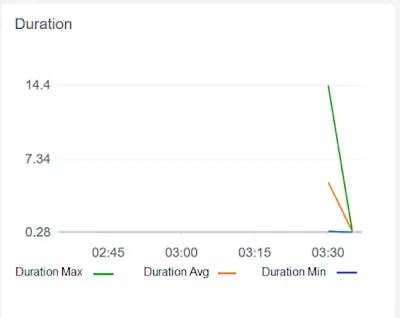
However, CloudWatch doesn’t tell us how much time each downstream call takes. This information is critical to setting a timeout limit for integrated services.
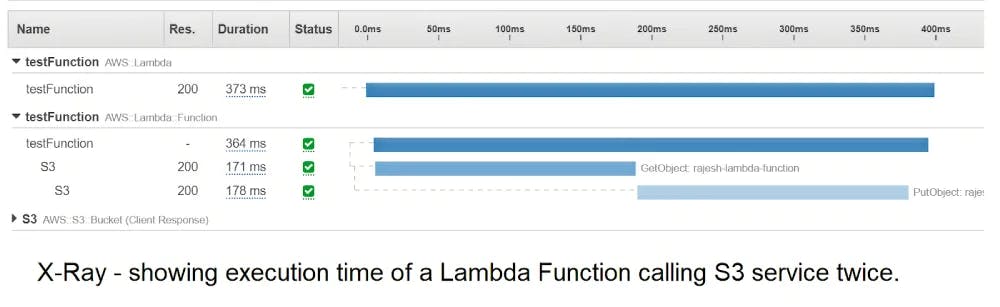
Amazon X-RAY Amazon X-Ray can help you discover the timeout value for downstream services. X-Ray shows the execution time taken by all downstream systems.
In the example below, it shows the execution time of S3 GET (171ms) and S3 PUT (178ms) requests.
1.4 AWS Lambda Timeout Deep Dive: Three Scenarios to Understand Timeout Behavior
Now, let’s take a few scenarios and understand how these AWS limits might cause timeout errors in a serverless application.
1.4.1 Scenario 1 - A REST API implemented through a Lambda Function is exposed through API Gateway.
This API is calling a third-party service to retrieve the data. But for some reason, this third-party service is not responding. The function has a timeout of 15 minutes, so the thread will be kept waiting for the response.
However, the threshold limit for API Gateway is 29 seconds, so the user will receive the AWS Lambda timeout error after 29 seconds. Not only is this a poor experience for the user but it will also result in additional cost.
Solution: For APIs, it’s always better to define your own timeouts at the function level, which should be very short – around 3-6 seconds. Setting the short timeout will ensure that we don’t wait for an unreasonable time for a downstream response and cause a timeout.
1.4.2 Scenario 2 - REST API is calling multiple services. It’s calling a DynamoDB table to retrieve data, calling an API, and then storing the data back in the DynamoDB table.
If the API is not responding, the function will wait for the response until it reaches the timeout set at the function level (let’s assume 6s), and then timeout. Here one integration point is causing the whole function to timeout.
Solution: For each integration point, the timeout needs to be set so that the function can handle the timeout error and process the request with the available data and doesn’t waste the execution time. So here, for all 3 integrations, the timeout limit has to be defined to handle the response in an effective way.
1.4.3 Scenario 3 - Using Fixed AWS Lambda timeout limit - A BADDDDD... APPROACH
To solve the above two problems, most developers use a fixed AWS Lambda timeout limit at the function and API Integration level hardcoded in the code/config.
However, it doesn’t make full use of the execution time and can cause problems.
If it is too short, it doesn’t give the request the opportunity to succeed. For example, there’s 6s left in the invocation but we had set timeout to 3s at the integration level.
If it is too long, the request will timeout at calling the function. For example. there’s only 5s left in the invocation but we had set timeout to 6 seconds at the integration level.
Let’s talk about the two general approaches to setting timeout values.
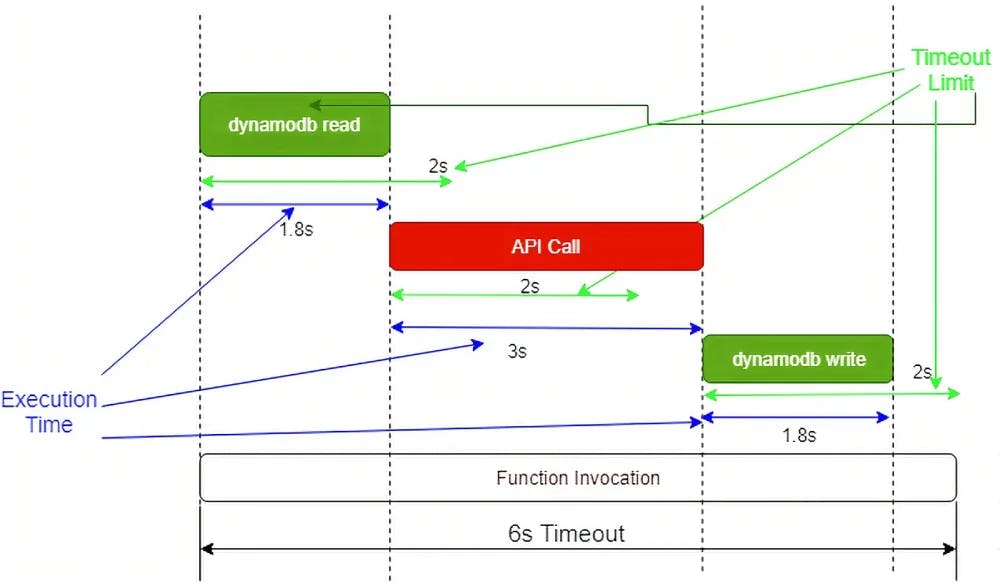
In the first approach, the function timeout limit is set as 6s and for each integration call (3x here- DynamoDBReadCall, APICall, DynamoDBWriteCall), it is set at 2s. Even though the whole function invocation (including all three calls) can be done within 6s, the API integration call will timeout as it is not able to perform within 2s. It has not been given the best chance to complete the request.
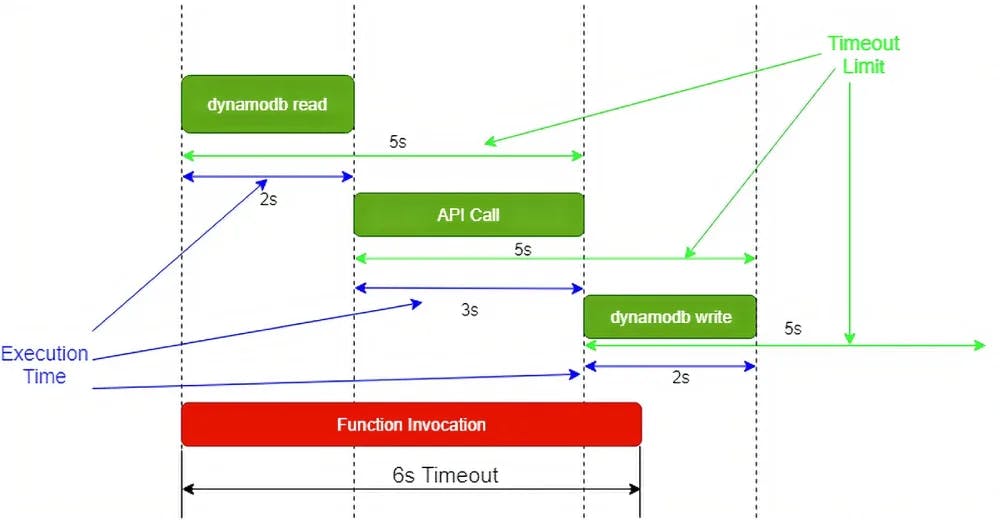
Similarly, in the second approach, if the timeout is set too high for each integration call (3x here- DynamoDBReadCall, APICall, DynamoDBWriteCall), it will cause the function to timeout without giving a chance for recovery. The function has a 6s timeout and each integration call has a 5s timeout. So, the whole execution can take a maximum of 15s + 1s (1s for handling the response at the function level). In this case, requests are allowed too much time to execute and cause the function to timeout.
Solution: To utilize the invocation time better, set the timeout based on the amount of invocation time left. It must also account for the time required to perform recovery steps, like returning a meaningful error or returning a fallback result based on circuit breaker pattern.
2. Conclusion
In this article, we’ve looked at various scenarios in which timeouts can lead to bad user experience, not to mention adding cost to your account. So, apply common sense. If a function is taking more time than allotted, there could well be a problem that needs proper attention, rather than simply increasing the timeout limit. Monitoring is the best way to identify these gaps and finetune timeout configuration.


